Manufacturing Product Configurator: How It's Revolutionizing Production and Mass Customization
In the age of batch-size-one, customers expect products tailored to their exact needs—without waiting months or paying a premium. A Manufacturing Product Configurator is the software backbone that makes that expectation feasible. It lets sales teams, distributors, and even end customers design and configure complex products within predefined engineering rules, then automatically generates the data production needs (BOMs, routings, pricing, drawings, even cut lists). The result: fewer errors, faster quote-to-order cycles, and a seamless path from "I want this" to "we built it."
This guide translates the buzzwords into operations reality. We'll define what a configurator is, explain how it works in manufacturing environments, highlight benefits and use cases, and outline a pragmatic implementation plan—plus a concise FAQ to capture common "People Also Ask" questions. If you're exploring manufacturing product configurator software, configure-to-order workflows, or a 3D product configurator for the manufacturing industry, you're in the right place.
What Is a Manufacturing Product Configurator?
A manufacturing product configurator is a rules-driven application that enables users to build valid product variants by selecting options (dimensions, components, materials, finishes, accessories) inside guardrails defined by engineering. In practice, it's a bridge between sales (what the customer wants) and operations (what the factory can produce), ensuring every configured order is technically feasible, correctly priced, and production-ready.
Modern solutions come in a few flavors:
Rules-Based (Logic/Constraints) Configurators
Eliminate invalid combinations (e.g., "motor A requires controller B when voltage is X").
Visual/2D Configurators
Let users toggle options while previewing updated drawings or rendered images.
3D Configurators
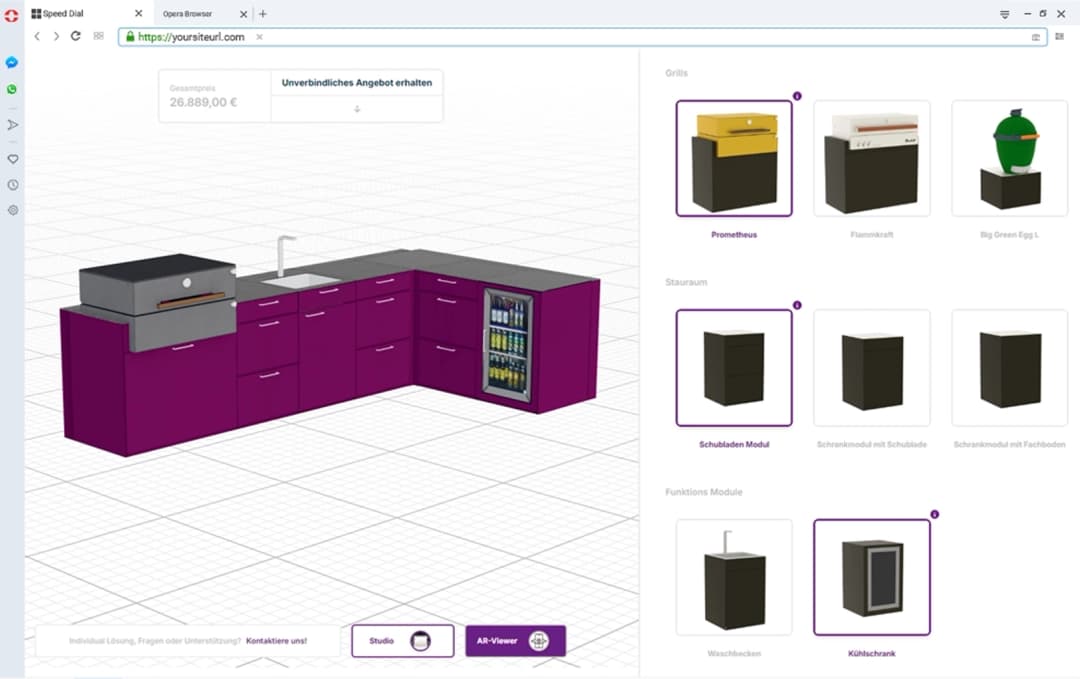
Provide real-time 3D views, exploded assemblies, and AR previews—critical for complex machinery, enclosures, workstations, or modular systems.
CPQ-Integrated Configurators
Tie configuration to pricing and quoting (Configure-Price-Quote), auto-calculating costs, margins, and discounts.
How Does a Configurator Work in Manufacturing?
Beneath the friendly UI is a chain of data transformations:
1. Product Model + Rules
Engineering codifies options, dependencies, dimensional ranges, tolerance rules, and safety constraints.
2. Guided Selection
The user chooses features; the configurator disables invalid options and alerts on conflicts.
3. Real-Time Pricing
The system recalculates pricing (materials, labor, overhead) and updates list price or customer-specific pricing.
4. Auto-Generated Outputs
Approved configurations produce the BOM, routing/operations, and manufacturing order meta-data; in advanced setups, CAD drawings and cut lists are generated on the fly.
5. Systems Handshake
The order syncs to ERP/MRP for procurement and production, to CRM for opportunity tracking, and to PLM/PDM (or storage) for drawings and revision history.
This end-to-end flow removes manual rework and miscommunications that traditionally occur between sales, engineering, and the shop floor.
Why Manufacturers Adopt Product Configurators (Top Benefits)
Faster Quotes, Faster Orders
Sales or channel partners can self-serve. Quotes that took days can drop to minutes—without engineering intervention for every variation.
Error Elimination and Rework Reduction
Rules prevent impossible specs; BOMs and routings align precisely to the chosen options. Fewer drawing revisions, fewer NCRs, fewer returns.
Mass Customization at Scale
Offer thousands (or millions) of valid combinations while maintaining standardization in parts, sub-assemblies, and operations.
Higher Win Rates and Bigger Baskets
Buyers see price impacts in real time and visualize trade-offs. That transparency builds confidence and typically increases average order value.
Production Alignment and Capacity Clarity
Every configured order already knows its materials and operations. Planners can evaluate capacity, lead times, and what-if scenarios more accurately.
Cleaner Data, Stronger Analytics
Structured configuration data feeds forecasting, cost analysis, and product roadmap decisions (e.g., which options actually sell).
Common Use Cases (with Examples)
Industrial Workstations & Tables
Select frame sizes, worktops, load ratings, drawers, lighting, power rails, and accessories; output BOM + cut list; visualize the final setup in 3D.
Machinery & Equipment
Configure motors, gearboxes, drives, guards, enclosures, control panels, and safety packages; auto-generate wiring and pneumatic options.
Enclosures & Cabinets
Parametric sizing, door types, hinges, vents, IP ratings; instant pricing based on sheet metal utilization and finishing.
Material Handling Systems
Conveyors with variable lengths, belts, supports, sensors; ensure safety compliance and capacity limits.
Furniture & Fixtures (B2B)
Modular components, fabrics, finishes; AR preview to validate fit and aesthetic in the final environment.
If 3D matters to the buying experience (complex geometry, spatial fit), a 3D manufacturing product configurator is a competitive advantage. If speed and accuracy matter most, a CPQ-first logic model with CAD automation may deliver the biggest ROI.
Product Configurator vs CPQ: What's the Difference?
- Configurator = "Can we build it?" (rules, constraints, variants, technical validity).
- CPQ = "Can we price and quote it profitably and quickly?" (cost/price logic, approvals, discounts, margin guardrails).
In practice, manufacturers get the best outcomes when the two are integrated: configure valid products, price them correctly, and route orders into ERP with zero swivel-chair work.
Integrations That Matter (ERP, CRM, PLM, E-commerce)
A manufacturing product configurator solution should plug into the systems you already use:
- ERP/MRP (e.g., Odoo, SAP, Microsoft, Infor): push BOMs, routings, work orders, reservations.
- CRM (e.g., HubSpot, Salesforce, Zoho): sync quotes, contacts, and deal stages.
- PLM/PDM/CAD: automate drawing generation and revision control for engineered options.
- E-commerce (Shopify, WooCommerce, Magento, Wix): enable self-serve B2B portals or controlled dealer portals with real-time pricing.
- PIM/DAM: keep specs, media, and documentation consistent across channels.
Look for open APIs and event webhooks. You want to automate handoffs from configure-to-order through to procurement and production—no exported spreadsheets or retyping.
Implementation Playbook (Practical Steps)
1. Define Scope and Value
Start with a product family where variety causes quoting delays or frequent mistakes. Quantify the impact (quote time, error rates, returns, margin leakage).
2. Model Rules and Options
Collaborate with engineering to codify constraints, parametric limits, and dependencies. Treat rules as product IP—versioned and tested.
3. Price Logic and Approvals
Encode cost roll-ups, margins, tiered discounts, and approval workflows. Decide what is dealer-visible vs internal.
4. UX and Visualization
If visual clarity drives confidence, prioritize a 3D view with real-time material/finish changes. Keep the UI guided: progressive steps, clear errors, instant feedback.
5. Outputs and Automation
Decide which artifacts must be generated automatically (BOM, routing, DXF/STEP, PDF cut sheets, labels). Map where they live (ERP, PLM, shared storage).
6. Integrations
Connect ERP/CRM/PLM early. A thin but working integration beats a perfect but delayed one. Validate data mapping with a sandbox environment.
7. Pilot, Measure, Iterate
Launch with a limited catalog and a small sales cohort or one distributor. Instrument the funnel (time to quote, conversion, average order value). Iterate on rules and UI.
8. Rollout & Governance
Train sales/channel, document exceptions, and assign ownership for ongoing rule maintenance. Create a change-control process for new options or price updates.
Who Benefits Most?
- Sales & channel partners: faster, self-serve quotes with fewer escalations.
- Engineering: fewer ad-hoc requests; time reclaimed for R&D.
- Operations & planning: cleaner demand signals and complete work order data.
- Finance: consistent margins, fewer credits/returns.
- Customers: transparency, confidence, and products that match expectations.
Whether you're a mid-market manufacturer or an enterprise with complex variants, configurators scale from simple option trees to deep parametric rules that touch CAD and PLM.
FAQs (People Also Ask)
What is a manufacturing product configurator?
A rules-driven tool that guides users to build valid product variants, then outputs pricing and production data (BOMs, routings, drawings) so the factory can make exactly what was ordered.
How does a product configurator enable mass customization?
By standardizing options and automating rules, it lets you offer many variations without reinventing engineering each time—maintaining efficiency at scale.
Is a configurator the same as CPQ?
No. The configurator ensures technical validity; CPQ handles pricing and quoting. Together, they deliver fast, accurate, profitable orders.
Can a configurator integrate with our ERP/CRM?
Yes. Leading platforms provide APIs to push orders, BOMs, and pricing into ERP/MRP and sync quotes and contacts with CRM.
Do only big manufacturers benefit?
SMBs benefit too—especially those with custom or semi-custom products where quoting is slow and errors are costly.
What types exist (2D, 3D, visual)?
From logic-only to 2D schematic to full 3D product configurator with AR. Choose based on product complexity and the importance of visual confidence.
How hard is implementation?
It's manageable with the right scope. Start with one product family, model rules, integrate minimally, and iterate. Expect measurable improvements in weeks—not years.
Choosing the Right Manufacturing Product Configurator Software
When evaluating manufacturing product configurator solutions, weigh these criteria:
- Rule engine depth: Can it handle parametric logic, dependencies, and dimensional constraints?
- Visualization quality: Do you need photoreal 3D and AR, or is schematic/2D enough?
- CPQ fit: Does it support margin rules, approvals, customer-specific pricing?
- Outputs: BOMs, routings, CAD, labels—generated automatically and consistently.
- Integrations: Prebuilt connectors or robust APIs for ERP, CRM, PLM, PIM, and e-commerce.
- Performance & UX: Real-time updates, mobile-ready, low friction for dealers and reps.
- Governance: Versioning, testing, and change control for rules and price logic.
- Scalability & TCO: Can it grow with your catalog complexity and volume without exploding costs?
If you're comparing options (e.g., "best product configurator software for manufacturing" or "manufacturing product configurator pricing"), request a guided demo with your real product constraints. A credible vendor should prototype a representative scenario and show the ERP handoff.
The Bottom Line
Customization isn't a nice-to-have—it's a market expectation. A Manufacturing Product Configurator operationalizes that expectation with speed and accuracy, from the first click to the finished product. Manufacturers that adopt configurators see faster quotes, fewer errors, higher conversion rates, and a tighter connection between sales and production. Whether your priority is 3D visualization, CPQ speed, or ERP automation, the path is clear: codify your rules, integrate your stack, and let customers build the product they actually want—confidently.
Ready to see a manufacturing configurator in action? Request a demo and we'll map your product family, show real-time pricing, and generate production-ready outputs in minutes.